EcoVadis provides sustainability ratings and intelligence used in global value chains, finance and commerce, offering detailed insights into environmental, social and ethical risks across more than 200 industry categories and 160 countries.
Sustainability offers a unique set of benefits and challenges.
Benefits:
- Reducing the risk of operational or supply chain disruptions.
- Protecting brands and company reputation
- Lowering costs through collaborative actions (e.g., reduction of energy consumption)
- Facilitating access to capital and increasing valuation (e.g., integration of ESG factors into investment decisions)
- Providing greater market access to consumers demanding green and responsible products and services.
Challenges:
- The proliferation of sustainability standards and labels;
- The internal change management needed to integrate sustainability into roles, processes and relationships;
- Challenges around engaging partners through common sustainability standards that create mutual value;
- A lack of internal ESG expertise and/or resources;
- The complexity of supply chains and/or business and investment networks.
Despite the many benefits and challenges of adopting sustainability practices, EcoVadis offers a valuable solution for navigating through these complexities. Its ratings allow procurement, finance, investment, banking, and other teams to monitor the sustainability performance of their portfolios and trading partners, fostering collaboration for continuous improvement.
EcoVadis Rating Methodology Overview and Principles
The EcoVadis rating methodology measures the quality of a company’s sustainability management system through its commitments/ policies, actions and results.
It is based on following seven foundational principles:
- Evidence based: The burden of proof is on the company being rated. It must provide supporting documents, such as commitments, certificates and KPI reporting, that showcase the maturity of its sustainability management system.
- Industry, Location and Size matters: The sustainability management system is assessed based on material industry issues, presence in risk countries and the size and geographical span of the company.
- Diversification of Sources: The rating is based not only on supporting documents provided by the company but also on information published by non-governmental organizations (NGOs), trade unions, international organizations, local authorities and other third-party organizations (e.g., auditors, CDP, external compliance database).
- Technology is a must: A rating system can only become reliable and robust if it is supported by technology. Technology facilitates industrialization, which enables fast learning, growth and scalability.
- Assessment by International Sustainability Experts: The supporting documents are analysed by a team of sustainability experts from around the globe who keep track of the latest best practices in sustainability.
- Traceability & Transparency: Every document used in the rating process is stored securely and can be traced. Rated companies have access to detailed results on each scoring decision.
- Excellence through continuous improvement: A company-wide quality management system supported by a client advisory board and a scientific committee.
EcoVadis Sustainability Management System
- EcoVadis considers an effective sustainability management system to be one that develops policies, implements actions and reports on results.
- These three management layers are further categorized into seven management indicators: Commitments, Endorsements, Actions, Certifications, Coverage – Deployment of Actions, Reporting KPIs and 360° Watch Findings (360) (Refer figure:1)
- These elements originate from the PDCA (plan–do– check–act) method, a four-step iterative process that forms the basis for a wide range of management standards around the world.
- Ecovadis Sustainability Management System consists of 21 Sustainability Criteria(Refer figure:2)
- To fully understand a company’s impacts, the assessment framework is customized based on its industry, size and operational locations.
- These parameters are identified when a company registers on the EcoVadis ratings platform and shape the questionnaire it subsequently receives.
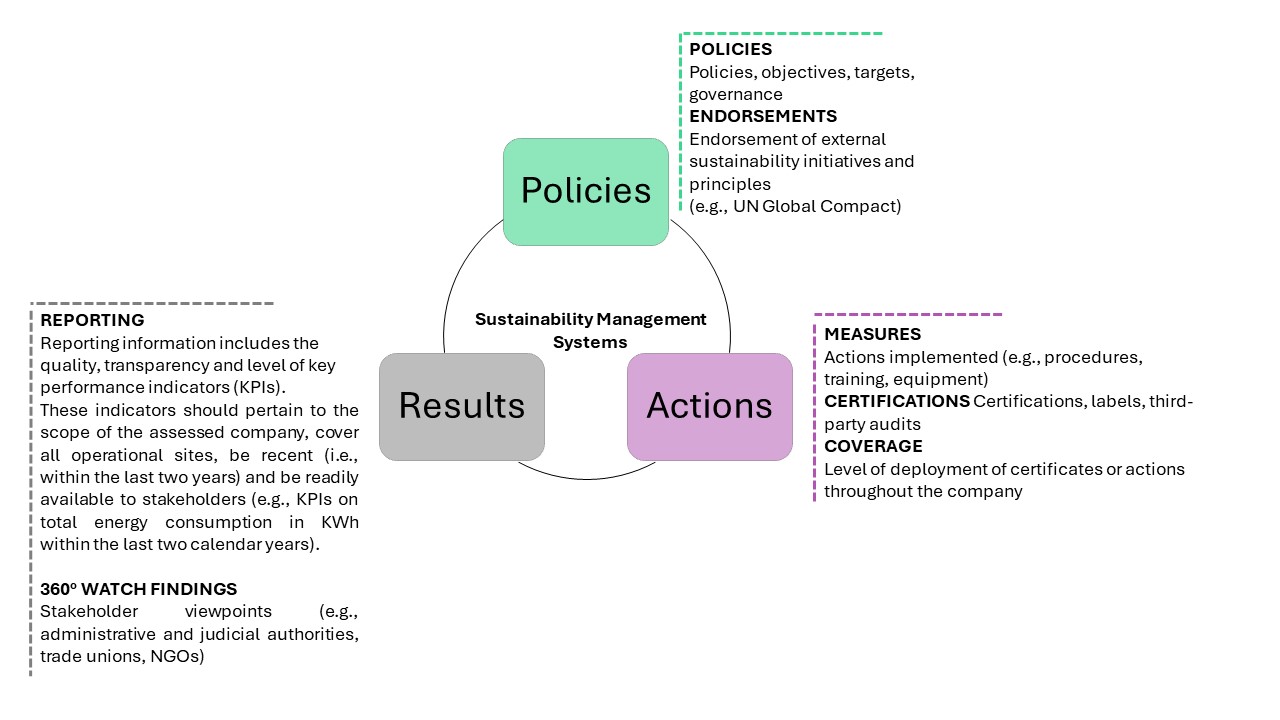
Figure 1
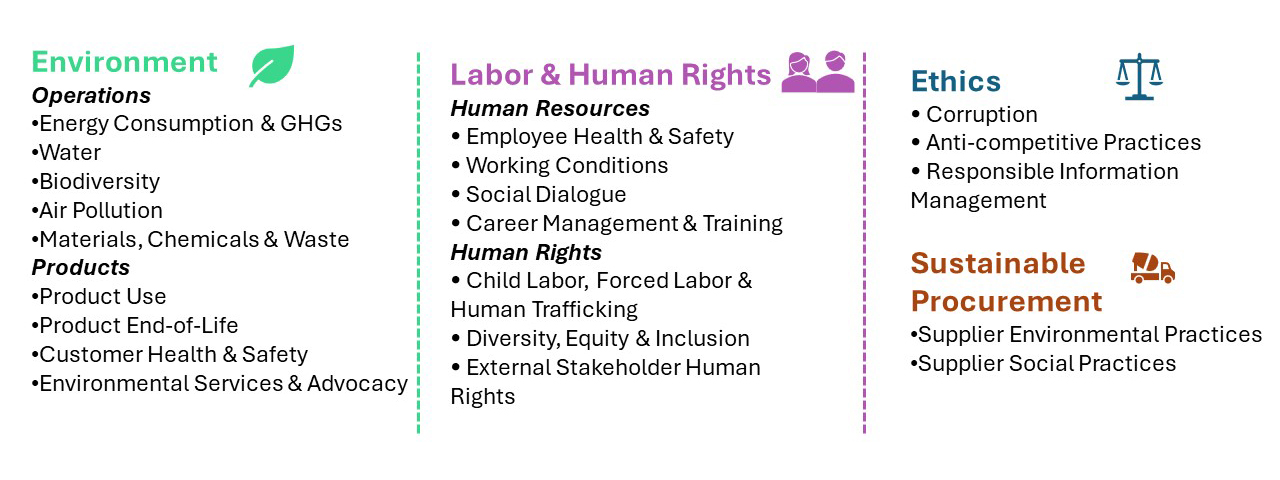
Figure 2
EcoVadis Ratings Process & Steps
- Onboarding: Online registration and qualification (e.g., industry, size, location) of all rated companies.
- Assessment: Sustainability expert analysis combining multiple data sources (e.g., online questionnaire, supporting documents, 360° Watch Findings).
- Results: Easy to use and dynamic scorecard available on the EcoVadis ratings platform. Quantitative and qualitative results published.
- Improvements: Online Corrective Action Plan feature available to drive continuous improvement.
Supporting Documents and Data
During the questionnaire process, EcoVadis requires companies to submit formal, recent and credible documentation related to their company’s sustainability management system. Few examples of supporting documentation are as follows:
- Policies and Actions not older than 8 years
- KPI reporting not older than 2years
- Not considered if policy document is issued less than one month before being submitted.
- Do not combine documents (ex. Mix of environment policies, risk assessment & training materials)
- Do not provide documents submitted for legal compliances (ex. Extract of law, legal compliance related audit)
- Should not include any charts, receipts or photos
Document Analysis
During this step, EcoVadis requires providing comprehensive and tangible evidences to support the declarations made in the questionnaire.
- Policies/ statement/qualitative objectives to improve sustainability. Few policies examples include:
- Overview of grievance mechanism or whistle blowing procedure to be detailed in the company’s code of conduct.
- Reporting channels
- Confidentiality Assurance
- Emergency response procedure document outlining actions to be taken in event of accident.
- Absolute/ Relative quantitative targets with defined timeframe
- Relevant sustainability issues addressed. Example of measures taken under sustainability procurement:
- Employees in procurement department have received training on sustainability issues in supply chains.
- Suppliers are audited on site.
- Sustainability objectives are integrated into performance reviews pf employees in procurement department of the company.
- Governance & Allocation of responsibilities defined
- Policies under each head: Environment, Labour & Human Rights, Ethics and Sustainable Procurement. Scope of policy to be particularly specified.
- Certifications: few examples include:
- ISO 140001, ISO 45001, ISO 27001, SA 8000, FSC, EU Ecolabel, MSC, VCA or SCC (SHE), RC 140001
- Company commitment to reduce energy consumption commitment in environment policy section of sustainability report.
- Greater than equal to 2 policies, Category: Good
- Greater than equal to 4 polices, Category: Advanced
- Greater than equal to 6 policies, Category: Outstanding
List of Documents that can be uploaded as part of supporting evidence:
- Annual Report with CSR integrated report
- Sustainability Report
- Code of ethics
- Sustainable Procurement policies
- Employee Handbook
- UNGC communication of progress
- Policies
Small sized organizations can also upload the following as part of supporting evidence:
- Invoice & Action Plans
- CSR project- Management committee
- Emails
- Training documentation
- Emission information from bills
Stakeholder Opinion- 360° Watch Findings
The methodology integrates thousands of external sources (e.g., NGOs, trade unions, international organizations, local authorities, auditors, and other third-party organizations) via our online smart- crawler tool (360° Watch Findings).
Some of the sources qualified to provide key information on everything from innovative practices used by companies to ethics issues and scandals:
International Labor Organization, AccountAbility (International), United Nations Environment Program and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (International).
EcoVadis may contract an independent auditor to conduct an on-site verification on the assessed company as a complementary part of the document- based assessment. The audits are conducted for internal quality assurance and methodology verification purposes.
Scoring Process
The scoring of the seven management indicators is based upon below strict scoring guidelines.

The seven management indicator scores will then generate a score for each theme based upon the weight allocated to each management indicator. The three management layers, commitments, actions and results are given the following respective weights: 25%, 40% and 35%
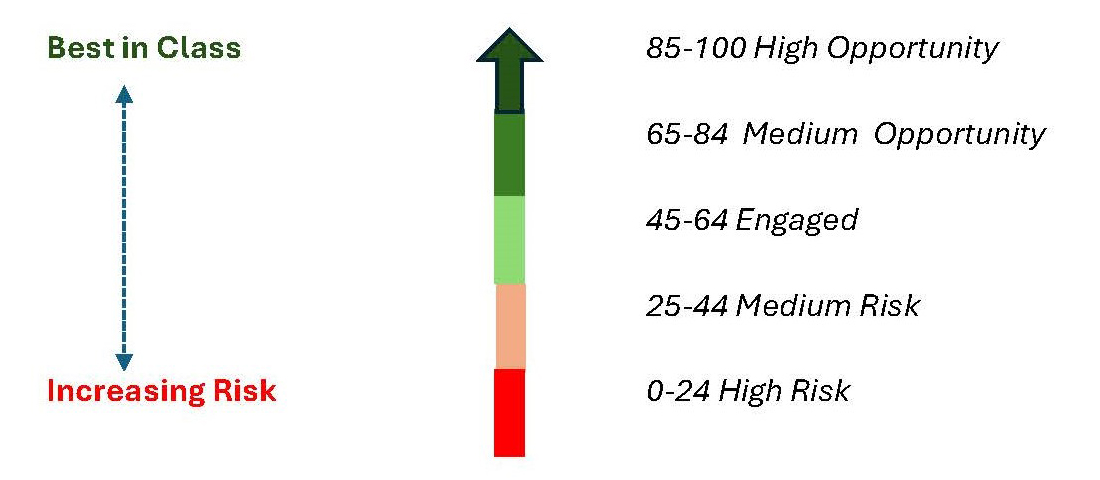
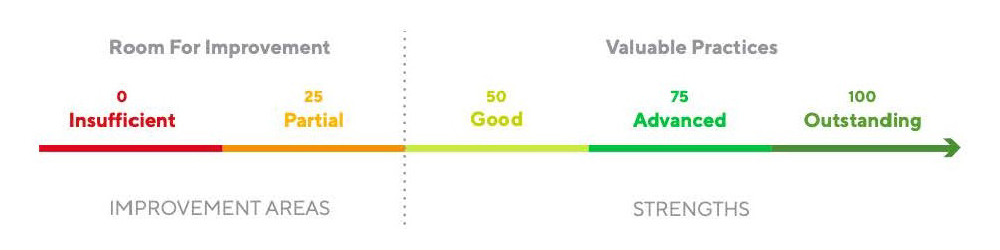
Scoring Scale
The assessment score enables companies to understand where their sustainability performance stands in absolute terms and to benchmark their performance against industry peers. The scoring scale is applicable for each theme and for the overall score. It has been intentionally designed to leave room for companies to improve their sustainability practices.
Strengths and Improvement Areas
In addition to scoring, a set of strengths and improvement areas are highlighted for each theme in the EcoVadis Scorecard.
Validation and Publication
When scoring is completed and the strengths and improvement areas are identified, the assessment enters the validation stage. The validation stage consists of verifying the methodology. Following the validation stage, a scorecard is published online for the organization.